In today’s lesson, we learned about the visibility graphics in Revit from the head honcho of Revit, Craig Meadows. We also got a chance to work with legends and schedules. There are a number of ways in which you can control the view settings in Revit: through the view toolbar on the bottom of the page, through view properties, or through visibility graphics.
 This toolbar on the bottom off the page contains a lot of the same things that view properties does in a convenient toolbar. It contains the scale, level of detail button (course, medium, or fine), display graphics (wireframe, hidden line, shading, or shading with edges), shadows button (which can slow your computer down if turned on all the time-use on a need basis), crop regions, temporary Hide, and a reveal hidden objects bar. Before getting into a project, a good method is to get used to these settings and decide personal preferences regarding viewing your project.
This toolbar on the bottom off the page contains a lot of the same things that view properties does in a convenient toolbar. It contains the scale, level of detail button (course, medium, or fine), display graphics (wireframe, hidden line, shading, or shading with edges), shadows button (which can slow your computer down if turned on all the time-use on a need basis), crop regions, temporary Hide, and a reveal hidden objects bar. Before getting into a project, a good method is to get used to these settings and decide personal preferences regarding viewing your project.
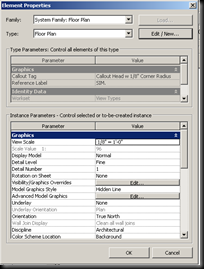
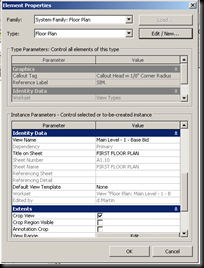
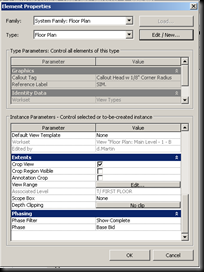
The view properties toolbar allows you to change some of the same types of things but also offers you options on how to use an underlay, extents, phasing, and much more. To get to this menu either right click on the view or type vp. An underlay is an option you can choose if you wish to see a floor plan on another one, like if you are on the bottom floor and want to see a grayed out version of the top. In extents, you can manage the view range, or the ability to change the extents of a certain view. The scope box is a way to take a 3D view and make only show portions of the drawing. You do this by positioning the box so that the element you want to see are in the box and the ones you don't want to see are not. This works great for 3D floor plans or axonometric sections.
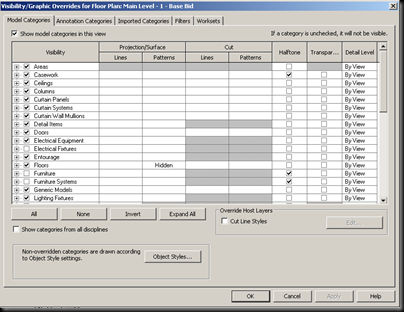
The visibility graphics is a way to control what and how you see elements in the view. The quick way to get to this menu bar is to type vg. The checkmarks along the left side of names of elements controls whether or not elements are to be shown in the view. In the model categories bar, you can control how model elements are shown. In the annotation categories, you control how annotation and dimensions are viewed. In imported categories tab, you can filter which imported files, like dwgs, are shown. In filters, you can create filters which manage which types of elements can be shown. And the worksets bar allows you to turn on and off worksets.
Legends are views which can be put into multiple sheets, unlike other views. In general they are ways to put notes in a consolidated location. You create a legend by going into view and create new, legend. When adding in legend components, they are not really components, but rather pictures of the component info. Legend tags are created by placing a symbol into the legend. In order to change the legend in any way, you must go to the family editor.
Area schedules are much like room schedules. They can be very important in the integration of program requirements, configuration of cost of building based on cost per square inch, or in indication of spacial requirements.
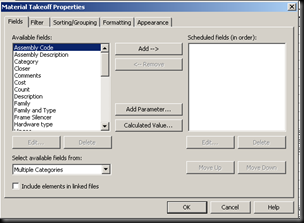
Material takeoff schedules pulls information from the project about the types of materials being used and is very helpful in computing material costs, quantities, and other helpful information.
Schedules allow a user to create a database of information drawn from the model in order to input it into third party programs or in order to compute necessary information about the project, which reduces amount of computing time.


 revit bootcampers - we are really really good looking
revit bootcampers - we are really really good looking